I. Introduction
In today’s technologically driven world, battery technology plays a pivotal role in powering a wide array of devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles. The capability to store and deliver energy efficiently is essential for our increasingly mobile and connected cultures.
Among the numerous types of batteries available, the 18650 battery stands out for its versatility and wide use across colorful disciplines. Initially developed for use in laptops, the 18650 battery has set up operations in everything from flashlights to electric vehicles. This composition aims to give a comprehensive description of the 18650 battery, covering its specialized specifications, operations, advantages, challenges, safety considerations, and unborn trends. By the end, compendiums will have a deeper understanding of this essential element of ultramodern technology.
II. Understanding the 18650 Battery
A. Description and introductory structure of the 18650 battery
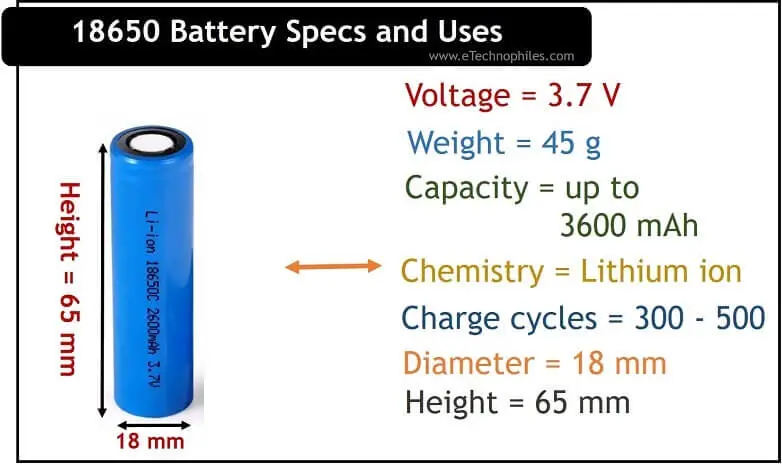
The 18650 battery, named for its confines( 18 mm in periphery and 65 mm in length), is a spherical rechargeable lithium-ion battery. Its introductory structure consists of an anode( generally made of graphite), a cathode( generally made of lithium cobalt oxide or lithium manganese oxide), and an electrolyte result. These factors are boxed in a spherical essence shell, with outstations at each end for connection to electrical circuits.

B. Literal background and development of the 18650 battery
The history of the 18650 battery dates back to the early 1990s, when it was first introduced by Sony for use in camcorders and laptops. Over time, advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have led to advancements in the performance, energy viscosity, and safety of 18650 batteries. At the moment, they’re one of the most extensively used types of rechargeable batteries in colorful electronic devices and operations.
C. Comparison with other battery types
Compared to other battery types, similar to nickel-cadmium ( NiCd) and nickel-essence hydride( NiMH) batteries, the 18650 battery offers several advantages. It has an advanced energy viscosity, meaning it can store more energy in a lower and lighter package. Also, 18650 batteries have a longer cycle life and a lower tone-discharge rate, making them ideal for operations requiring long-term trustability and performance.
III. Technical Specifications of 18650 Batteries
A. Confines and physical characteristics
The 18650 battery is characterized by its specific confines, with a periphery of 18 millimeters and a length of 65 millimeters. These standardized confines allow for interchangeability and comity across different biases and operations. also, the physical characteristics of the battery, similar to its weight and shape, contribute to its felicity for colorful electronic bias and systems.
B. Capacity( mAh) and energy viscosity
Capacity, measured in milliampere-hours ( mAh), is a pivotal specification of 18650 batteries. It indicates the quantum of charge the battery can store and later deliver. Advanced capacity 18650 batteries can give longer runtime between charges, making them ideal for high-demand operations similar to electric vehicles and movable electronic bias. Energy viscosity, expressed in watt-hours per kilogram( Wh/ kg), is another important parameter that reflects the quantum of energy stored per unit of weight.
C. Voltage and discharge rates
The voltage of an 18650 battery generally ranges from 3.6 to 4.2 volts, depending on its state of charge. This voltage position is compatible with the utmost electronic bias and circuits that bear a stable power force. Discharge rates, frequently expressed in terms of C-standing, indicate the maximum current that the battery can safely deliver over a specified period. Advanced discharge rates are suitable for operations with high power conditions, similar to power tools and electric vehicles.

D. Charging styles and cycles
Charging styles for 18650 batteries vary depending on the specific chemistry and manufacturer recommendations. Common charging styles include constant current( CC), constant voltage( CV), and palpitation charging. The charging cycle refers to the process of charging and discharging the battery over its lifetime. Proper charging methods, including avoiding overcharging and icing balanced charging across multiple cells in a battery pack, are essential for maximizing battery performance and life.
IV. Operations of 18650 Batteries
A. Consumer electronics (e.g., laptops, flashlights, power banks)
18650 batteries are extensively used in consumer electronics due to their high energy viscosity, compact size, and rechargeable nature. They power a variety of devices similar to laptops, flashlights, and power banks, furnishing a movable and dependable energy storehouse for everyday use. The versatility and comity of 18650 batteries make them a popular choice among manufacturers and consumers.

B. Electric vehicles (e.g., electric buses, e-bikes)
In the automotive industry, 18650 batteries play a pivotal role in powering electric vehicles( EVs) and electric bikes (e-bikes). Their high energy viscosity and capability to deliver high power affairs make them well-suited for furnishing the necessary propulsion for EVs, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. E-bikes also profit from 18650 batteries, furnishing riders with effective and sustainable transportation options.
C. Renewable energy storehouse (e.g., solar power systems)
Renewable energy storehouse systems, similar to solar power systems, frequently use 18650 batteries to store redundant energy generated from renewable sources like solar panels. These batteries act as a buffer, storing energy during ages of redundant generation and releasing it when demanded, furnishing a dependable and sustainable energy storehouse for out-of-grid and grid-tied operations. The scalability and modularity of 18650 battery packs make them ideal for renewable energy storehouse operations.
V. Future Trends and inventions
A. Emerging trends in 18650 battery technology
Arising trends in 18650 battery technology include advancements in accouterments, similar to the development of new electrode accouterments and electrolytes. Experimenters are exploring ways to enhance energy viscosity, ameliorate cycle life, and increase safety. Also, there is a growing focus on sustainable manufacturing processes and recyclability to reduce environmental impact.
B. Inventions driving advancements in performance and effectiveness
Inventions driving advancements in performance and effectiveness involve new manufacturing methods, such as roll-to-roll processing and 3D printing, which enable cost-effective products of high-quality battery factors. Similarly, advancements in battery operation systems( BMS) and smart charging algorithms are enhancing the overall effectiveness and lifetime of 18650 batteries.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, the 18650 battery stands as a foundation of ultramodern technology, powering a vast array of applications and operations across disciplines. Its compact size, high energy viscosity, and rechargeable nature make it necessary in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, medical applications, aerospace, and military operations. As we continue to witness advancements in battery technology, the future of the 18650 battery looks promising, with inventions driving advancements in performance, effectiveness, and sustainability, shaping a further galvanized and connected world.




