Zero_Speed_Switch
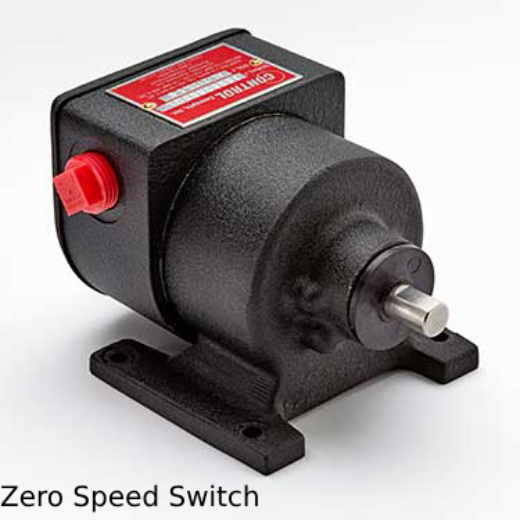
Introduction of Zero Speed Switch
A zero speed switch, or ZSS, is a crucial part of many industrial systems that are intended to identify when rotating machinery is in motion or stopped. Its main function is to keep an eye on machinery and equipment speed in order to give control systems valuable input. Zero speed switches are crucial for accident prevention, process optimization, and maintaining operational integrity in industrial settings where safety, dependability, and efficiency are of the utmost importance.
Operating Principle of Zero Speed Switch
A. Explanation of how zero speed switches detect motion cessation
Zero-speed switches use a variety of detecting techniques, including mechanical, optical, and magnetic ones, to identify when motion stops. The purpose of these switches is to keep an eye on the rotation of machine components like gears and shafts. The zero-speed switch indicates that there is no motion when the rotation speed drops below a predefined threshold or stops entirely. It does this by sounding an alert or starting a predefined action. This feature is essential for preventing mishaps, equipment damage, and production issues in industrial settings where sudden mechanical stops might result in inefficiencies or safety risks.
B.Overview of the technology and sensors used in zero speed switches
Zero-speed switches detect stoppages precisely by utilizing a range of technologies and sensors. Magnetic zero-speed switches employ magnetic fields to sense whether ferrous material is present on spinning parts or not. A light beam is employed by optical switches to identify interruptions brought on by stationary objects in their path. Mechanical switches detect variations in rotational speed by means of physical processes like centrifugal forces or spring levers. Zero-speed switches may now reliably and accurately report on the state of rotating machinery’s operation thanks to these technologies, which makes it easier to schedule maintenance and interventions in a timely manner to maintain output and safety.
Features and Functions of Zero Speed Switch
1. Speed Detection: The zero speed switches’ main job is to alert users when the shaft or equipment speed drops below a preset limit, which is typically zero rpm. They can correctly determine when there is no motion or when there is a slowdown in speed, indicating possible issues or anomalous operating situations.
2. Output Signals: When zero-speed conditions are identified, zero-speed switches usually give output signals, such as relay contacts or digital signals, to start processes, sound alarms, or engage safety devices. For automatic reaction, these signals can be interfaced to PLCs (programmable logic controllers), SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) systems, or control systems.
3. Adjustability: A lot of zero-speed switches have threshold, delay time, and sensitivity settings that can be changed, enabling users to customize the device to meet the needs of a particular application. This adjustability boosts adaptability and enables fine-tuning for best results in various operating scenarios.
4. Fail-Safe Operation: Zero-speed switches frequently have fail-safe features that trigger safety measures in the event of an equipment malfunction or a power outage in order to guarantee dependability and safety. This includes features that allow users to enter a safe default state or set off alarms to alert operators to possible issues.
5. Integration: Zero-speed switches can be easily included into pre-existing machine settings or control systems. They can be readily connected to PLCs, SCADA systems, or other monitoring and control devices for centralized management and data logging. They are compatible with a wide range of communication protocols.
Applications of Zero Speed Switch
A. Industrial machinery and equipment where zero speed switches are utilized
In many types of industrial machinery and equipment, precise rotational motion monitoring is crucial for both safe and effective operation. This is where zero-speed switches find their widespread application. These include rotating equipment used in mining, manufacturing, food processing, material handling, including conveyors, crushers, mixers, pumps, and fans. Zero-speed switches minimize downtime, avoid equipment damage, and guarantee smooth operation by detecting motion stoppage and generating alarms or launching remedial action as needed.
B. Safety systems and controls enhanced by zero speed switches
Zero-speed switch integration can be very beneficial for safety systems and controls in industrial settings. Through the monitoring of the rotational speed of vital machine components and the prompt detection of any deviation or halt, these switches significantly contribute to the improvement of safety measures. Zero-speed switches are crucial for ensuring that equipment is working within safe bounds in applications including emergency stop systems, interlocks, and protective devices. This lowers the possibility of mishaps, injuries, and expensive failures.
Benefits and Limitations of Zero Speed Switch
A. Advantages of using zero speed switches in various industries
Numerous benefits are provided by zero-speed switches across several sectors. First of all, they make it possible to reliably and accurately identify motion stoppage, protecting machinery and averting harm. Second, by reducing downtime brought on by equipment glitches or breakdowns, they aid in boosting production. Zero-speed switches also aid in the prediction of maintenance tasks, keeping an eye on the condition of the machinery and enabling replacement or preventative repair before major breakdowns happen. Furthermore, by enabling automated control and feedback systems and optimizing processes and resource utilization in industrial installations, these switches enhance operational efficiency.
B. Common challenges or limitations associated with zero speed switches
Indeed with all of their benefits, zero- speed switches come with some downsides and difficulties. A current constraint is the necessity for exact installation and estimation to guarantee precise functioning. Inaccurate installation or estimation may lead to false admonitions or an incapability to identify stir conclusions, jeopardizing safety and responsibility. Another difficulty is the switch’s vulnerability to external rudiments that can impact its performance and responsibility, similar to vibration, moisture, and temperature swings. Likewise, in order to retain optimal operation, zero- speed switches may need to be calibrated and maintained on a regular basis. This might result in increased operating charges and time-out.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zero-speed switches are crucial parts of industrial automation systems because they offer crucial monitoring and control features that guarantee the equipment and machinery operate safely and effectively. Their function in identifying zero-speed conditions and initiating relevant actions highlights their significance in averting mishaps, diminishing idle time, and enhancing overall efficiency. Zero-speed switches are still necessary to achieve operational excellence and preserve a safe working environment, even as companies depend more and more on automation to boost competitiveness and streamline operations.